The National Energy Board (NEB) was established 1959. The NEB was responsible for the import and export of energy, international and interprovincial pipelines and international power lines (see Electric-Power Transmission). In 2019, the NEB was replaced by the Canada Energy Regulator (CER). Regulations made under the NEB remain in effect under the CER.

Background
National Energy Board
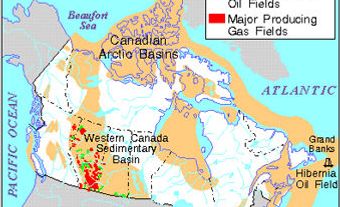
The NEB was established 1959 under the National Energy Board Act. The board was responsible for authorizing the export of oil, natural gas and electricity, the import of gas, the construction and operation of interprovincial and international pipelines, international power lines and designated interprovincial power lines, and the setting of tolls and tariffs for oil and gas pipelines (see Electric-Power Transmission). It also had regulatory responsibilities under the Canada Oil and Gas Operations Act for oil and gas activities on Canada's frontier lands.
The Board had an advisory function and could, on its own initiative, hold inquiries and conduct studies on specific matters and prepare reports for the information of the federal government, of Parliament and of the general public. It administered the National Oil Policy (1961-74) and the National Energy Program (1980-85).[6] (See also Oil and Gas Policy in Canada, 1947-80.) Over the years, the board's advisory role declined in importance as the federal government relied increasingly on its civil service for energy policy. The Board had all the powers vested in a superior court of record and reported to Parliament through the Minister of Natural Resources.
Canada Energy Regulator
On 28 August 2019, the Canadian Energy Regulator Act came into effect and the NEB was replaced by the CER. Like the former NEB, the CER is an independent federal agency that regulates pipelines that cross inter-provincial and international boundaries. As part of its responsibilities, the CER reviews applications for new pipeline projects as well as the design, construction or abandonment of pipelines. The CER also regulates the export and import of natural gas and the export of oil.
Did you know?
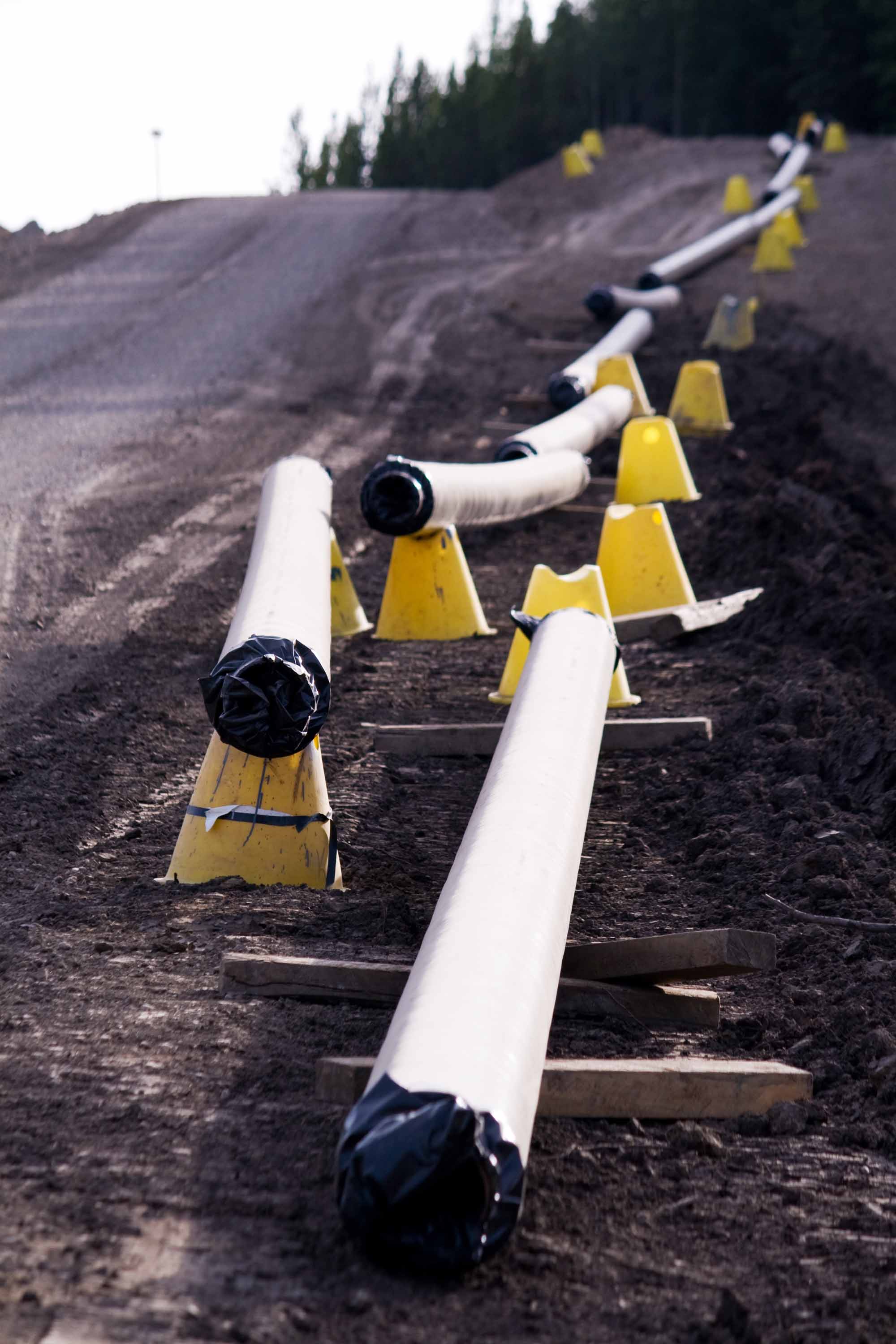
There are approximately 840,000 kilometers of pipelines across Canada. Of this amount, the CER regulates 73,000 kilometers.
Electricity exports are also regulated by the CER. To regulate electricity exports, the CER monitors the construction, operation and abandonment of international and inter-provincial power lines (see Electric-Power Transmission).

 Share on Facebook
Share on Facebook Share on X
Share on X Share by Email
Share by Email Share on Google Classroom
Share on Google Classroom




_IMO_9785756,_Maasmond_pic.jpg)